Benefit Sharing and Bioresource Traceability
Digital Application to Trace the Origin of Bioresources
Author: Shreyas Bhartiya
India’s Biological Diversity Act recognises the crucial role of local communities in conserving and managing bioresources that occur in their vicinity. Their lives are closely interlinked with these bioresources which serve as an important source of food and livelihood. The provision of Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) in the Biodiversity Act is a key tool to empower such communities to generate resources for the management of their local biodiversity.

Ensuring fair and equitable sharing of benefits for conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity is one of the core objectives of the Biodiversity Act. To fulfil this objective, identifying the benefit-claimers with whom these benefits or ABS is shared requires tracing the origin of the bio-resource to the place of genesis. However, lack of traceability in the supply chain doesn’t allow either the State Biodiversity Boards (SBBs) or companies trace the origin of a bio-resource. So, a User may have fulfilled their ABS obligations, but the benefits may still not to reach the communities.
The Bioresource Utilisation Traceability System (BUTS) is an application developed under the scope of the ABS Partnership Project to support SBBs to determine traceability of an accessed bioresource at the level of local communities who collect and supply such bioresources to traders and manufacturers.
As per the Biological Diversity Act, an SBB needs to consult with the Biodiversity Management Committees (BMC) before granting access to a User to access bioresources in the BMC’s jurisdiction. This consultative process allows the BMC to represent the community and safeguard the rights of the local people. The BUTS application facilitates increased collaboration and communication between the SBB and BMC. Its other features include a user-friendly interface, analytical features and real-time updates which allow effective coordination between the SBB and BMC in the monitoring of bioresources.
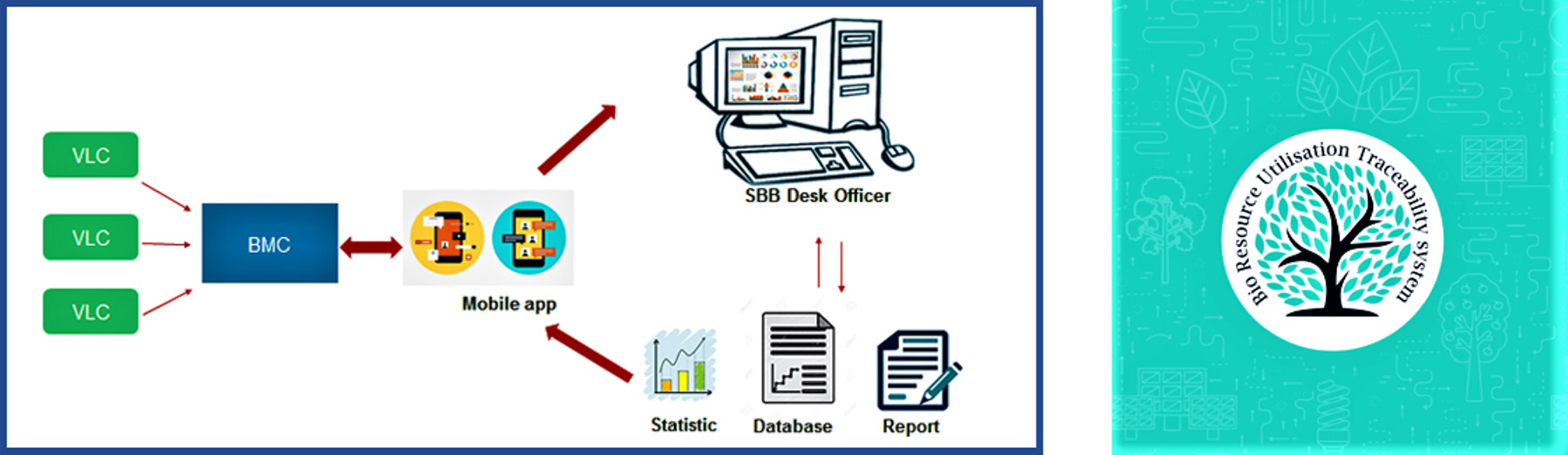 BUTS – Information Flow
BUTS – Information Flow
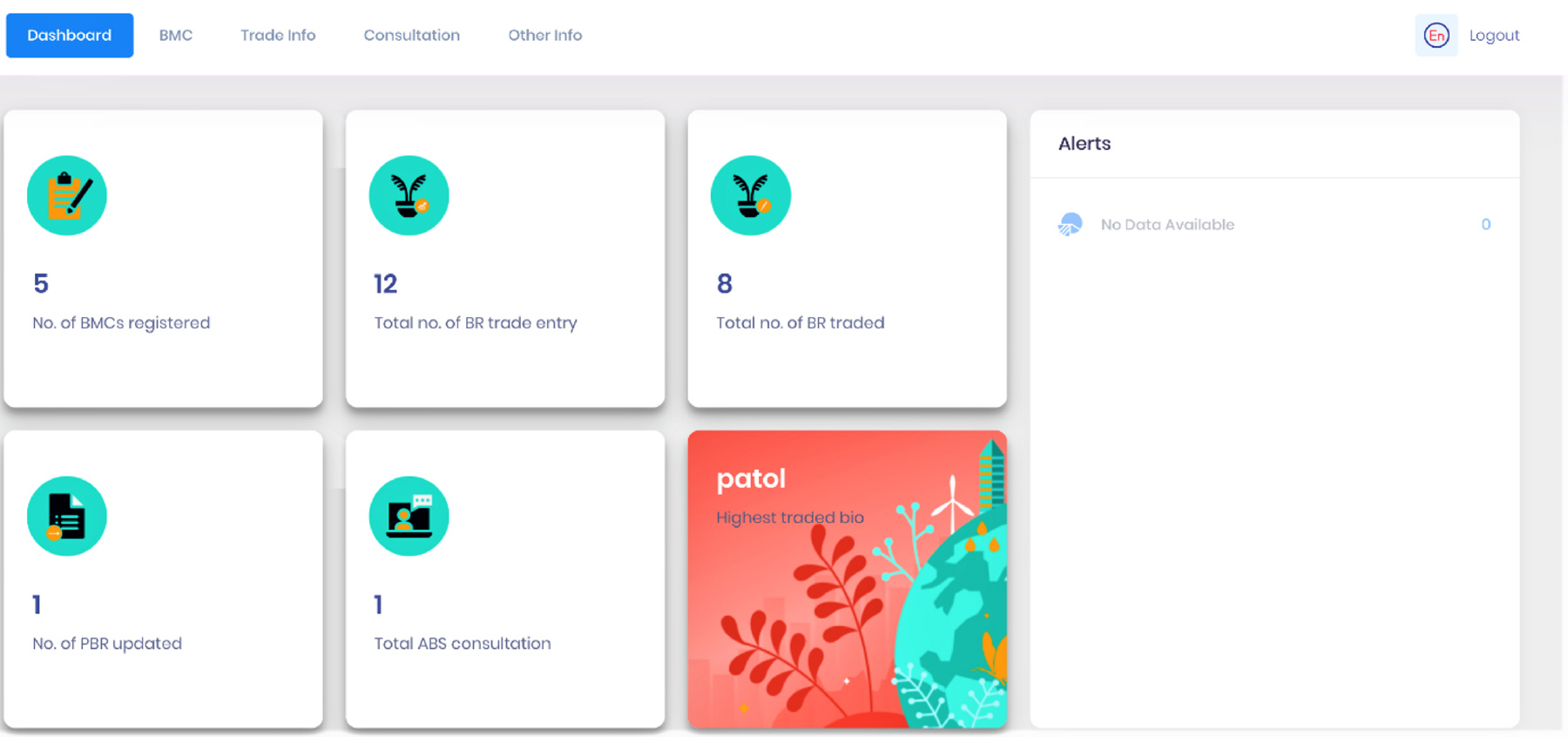 SBB Dashboard – BUTS Application
SBB Dashboard – BUTS Application
But the App requires active community mobilisation and participation of Village Level Committees involved in the trade of bio-resources to be more effective. It also needs an incentive mechanism for the BMC to capture and share the trade-related transactions with the SBB via the App. The SBB can then monitor and track those companies into fulfilling their ABS obligations.
The BUTS application, along with the developed Good Practice of creating synergies amongst Village Level Committees, provides an important tool in addressing the challenge of traceability. Going ahead, it will be interesting to see how BUTS is integrated into the working scope of many Indian SBBs for identifying and sharing the benefits with the true custodians of our biological diversity in the spirit of the Biological Diversity Act.
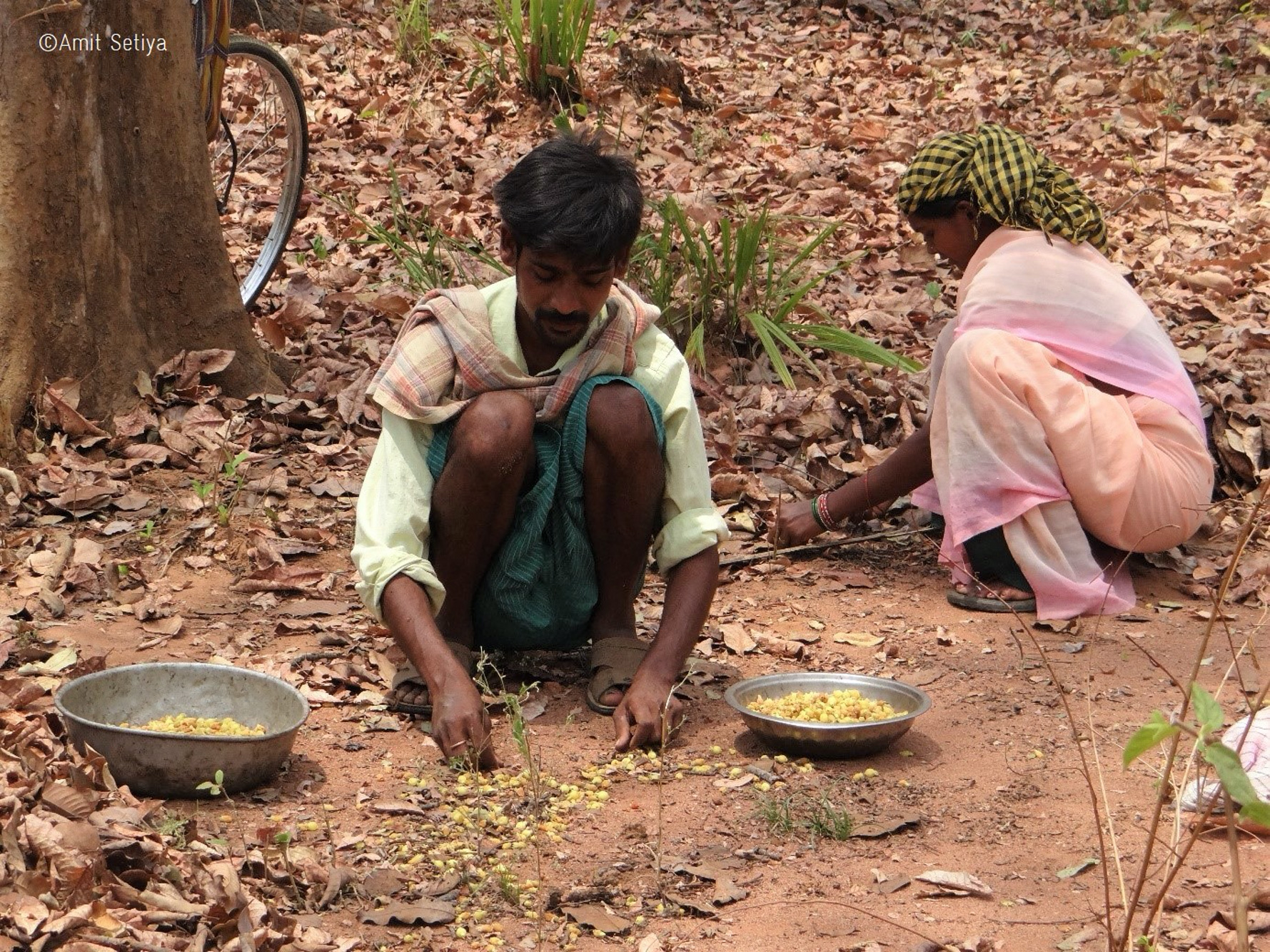 Tribal couple collecting Mahua flowers (Madhuca Longifolia)
Tribal couple collecting Mahua flowers (Madhuca Longifolia)

